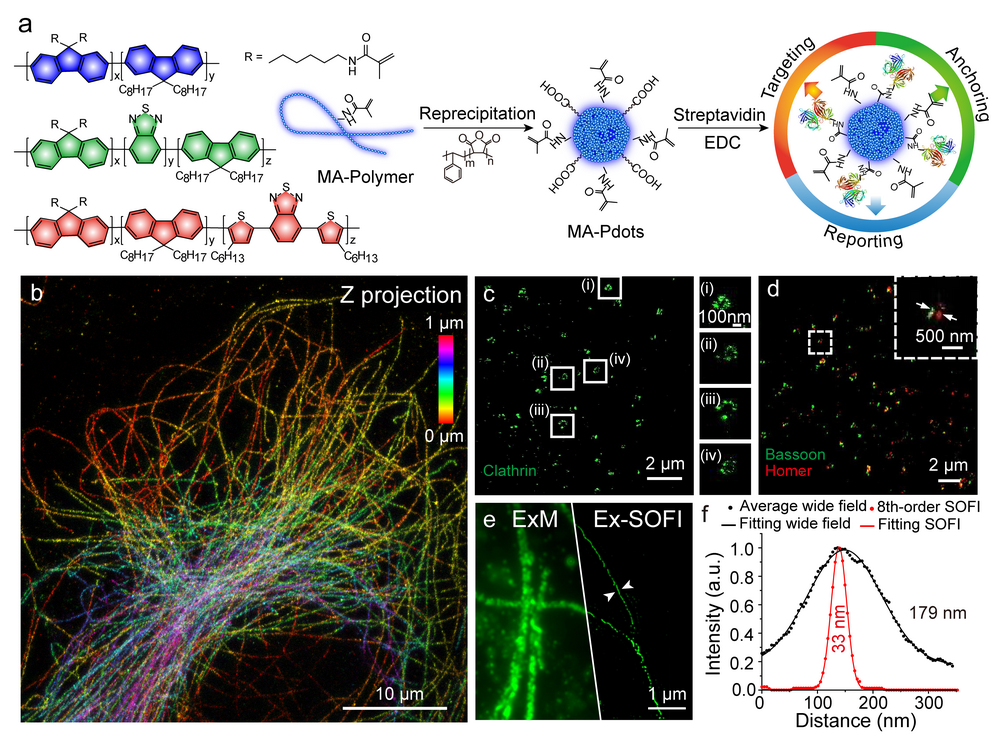
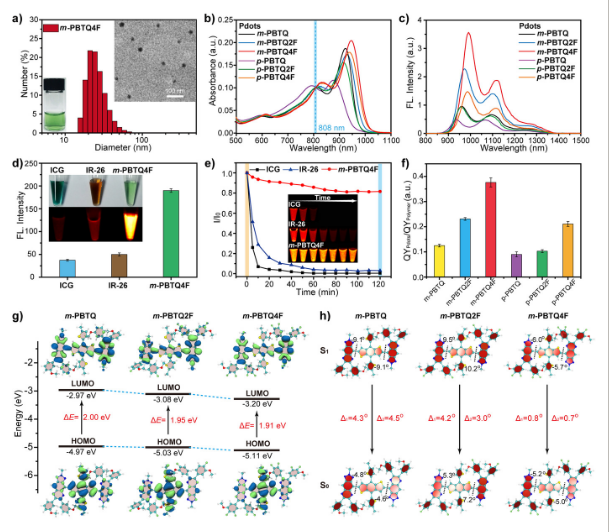
Fluorination Enhances NIR‐II Fluorescence of Polymer Dots for Quantitative Brain Tumor Imaging (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(47): 21049-21057)
Here, we describe a fluorination strategy for semiconducting polymers for the development of highly bright second near‐infrared region (NIR‐II) probes. Tetrafluorination yielded a fluorescence QY of 3.2 % for the polymer dots (Pdots), over a 3‐fold enhancement compared to non‐fluorinated counterparts. The fluorescence enhancement was attributable to a nanoscale fluorous effect in the Pdots that maintained the molecular planarity and minimized the structure distortion between the excited state and ground state, thus reducing the nonradiative relaxations. By performing through‐skull and through‐scalp imaging of the brain vasculature of live mice, we quantitatively analyzed the vascular morphology of transgenic brain tumors in terms of the vessel lengths, vessel branches, and vessel symmetry, which showed statistically significant differences from the wild type animals. The bright NIR‐II Pdots obtained through fluorination chemistry provide insightful information for precise diagnosis of the malignancy of the brain tumor.
The full details of the publication can be found here:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.202007886