NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging Reveals Bone Marrow Retention of Small Polymer Nanoparticles (Nano Letters , 2021, 21(1) :798–805)
The concept that systemically administered nanoparticles are highly accumulated into the liver, spleen and kidney is a central paradigm in the field of nanomedicine. Here, we report that bone is an important organ for retention of small polymer nanoparticles using
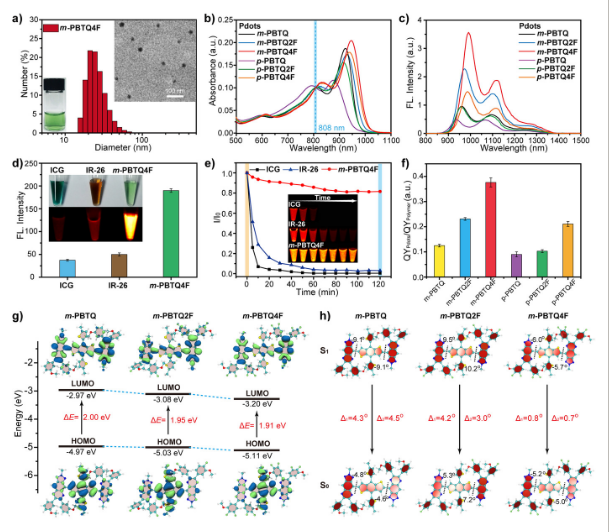
Fluorination Enhances NIR‐II Fluorescence of Polymer Dots for Quantitative Brain Tumor Imaging (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(47): 21049-21057)
Here, we describe a fluorination strategy for semiconducting polymers for the development of highly bright second near‐infrared region (NIR‐II) probes. Tetrafluorination yielded a fluorescence QY of 3.2 % for the polymer dots (Pdots), over a 3‐fold enhancement compared to non‐fluorinated counterparts.
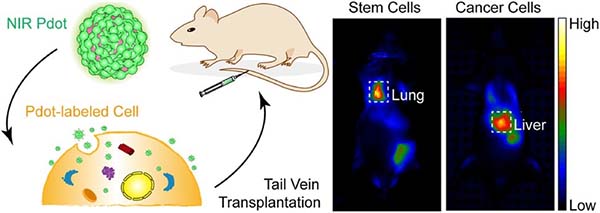
In vivo dynamic cell tracking with long-wavelength excitable and near-infrared fluorescent polymer dots (Biomaterials, 2020, 254, 120139.)
Development of cell-based therapeutic systems has attracted great interest in biomedicine. In vivo cell tracking by fluorescence provides indispensable information for further advancing cell therapy in clinical applications. However, it is still challenging in many cases because of the limited
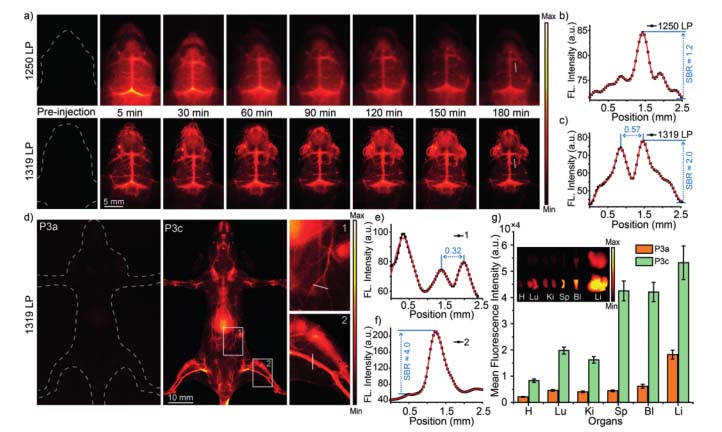
Semiconducting Polymer Dots with Dual‐Enhanced NIR‐IIa Fluorescence for Through‐Skull Mouse‐Brain Imaging (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2020,59(9):3691-3698)
Fluorescence probes in the NIR-IIa region show drastically improved imaging owing to the reduced photon scattering and autofluorescence in biological tissues. Now, NIR-IIa polymer dots (Pdots) are developed with a dual fluorescence enhancement mechanism. First, the aggregation induced emission of